HuiZhou Superpower Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.spchargers.com
Electrical instrumentation_Electrical common instrumentation_Multi-function electric instrument brand
When it comes to electrical measurements, there’s an array of tools that electricians frequently use, ranging from AC and DC current meters, voltmeters, and power meters to electricity meters, phase meters, power factor meters, multimeters, insulation resistance meters, grounding resistance meters, clamp meters, single and double bridges, resistance boxes, electrostatic voltmeters, and more. These instruments are essential for any electrician's toolkit. Have you ever wondered about the features and brands associated with these devices? I’ve taken the liberty of searching the web for some relevant information to help my fellow electrician friends.
The variety of electrical instruments can be categorized into different types:
1. Electrical measuring instruments
2. Electrical indication instruments
3. Digital electrical measuring instruments
4. Recording electrical measuring instruments (including statistical voltmeters)
5. Electricity meters (including maximum demand electricity meters, time-sharing electricity meters, multi-rate electricity meters, multifunctional electricity meters, standard electricity meters, etc.)
6. Electricity metering devices (including power load monitoring devices)
7. Current and voltage transformers (including measuring transformers, standard transformers, calibrators, and load boxes)
8. Transforming instruments (including power transmitters, AC sampling, and measuring devices)
9. Secondary circuits of electrical measurement systems (including PT secondary circuit voltage drop test devices)
10. Electrical measurement standard devices
11. Electricity metering and billing systems
12. Electrical testing instruments (including relay protection testers, high-voltage measurement test equipment, etc.)
Among the most commonly used electrical instruments are:
1. Ammeter
An ammeter (as shown in Figure 1) is divided into DC and AC types. When using an ammeter, it’s crucial to choose the correct range and connect it in series with the actual circuit being measured. The current flows into the meter through the "+" terminal and out through the "-" terminal. Wiring should be done under power-off conditions. DC ammeters cannot be used on AC circuits.

2. Clamp Meter
Clamp meters, also known as clamp-on ammeters (Figure 2), come in both AC and AC-DC varieties. When using them, check the meter's voltage rating against the line or equipment you’re measuring. Always set the range dial to a value greater than or equal to the expected current. Before taking a measurement, estimate the current or voltage, or start with a larger range and adjust based on the initial reading. Ensure the jaws are open when changing ranges. Under no circumstances should you change the range with power on. Place the wire to be tested in the center of the jaws and close them securely during measurement.
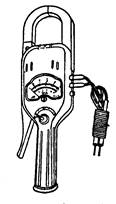
3. Voltmeter
The voltmeter (Figure 3) is available in both DC and AC versions. Select the appropriate range and connect the voltmeter in parallel across the circuit to be measured, ensuring the "+" and "-" terminals are correctly aligned. Wiring should be performed under power-off conditions. Never use a voltmeter in series within the circuit.

4. Multimeter
Also known as multitesters, multimeters (Figure 4) can measure DC current, AC current, DC voltage, AC voltage, resistance, capacitance, transistor parameters, and audio levels. They come in both analog and digital forms. Always perform a zero adjustment before each measurement. Be mindful of the range and the unit settings.

5. Insulation Resistance Meter
Also referred to as megohmmeters or shakers (Figure 5), they can be either hand-cranked or transistor-operated. When using an insulation resistance meter, ensure the range does not exceed the expected insulation resistance to avoid large errors. Power must be disconnected from the device under test, and it should be grounded to ensure safety.
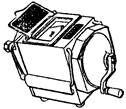
6. Electricity Meter
Electricity meters (Figure 6) measure energy consumption over a specific period. They include active and reactive energy meters. Active energy meters are further divided into single-phase and three-phase types. When using an electricity meter, ensure it matches the rated voltage and current of the circuit being tested and follow the wiring instructions on the meter's nameplate.

In terms of brands, here are ten domestic multi-function instrument brands worth noting:
- Xi’an Wesson Electric Co., Ltd.
- Shennian Power Technology Co., Ltd.
- Fuling Aobosen Electric Factory
- Nanjing Nengbao Electric Co., Ltd.
- Zhuhai Snowova Technology Co., Ltd.
- Suzhou Langlis Electronic Technology Co., Ltd.
- Changzhou Sanhe Sound Source Ultrasonic Technology Co., Ltd.
- First Planning Company
- Jiangsu Ankerui Electric Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
- Shenzhen Guodian Xuzhen Electric Technology Co., Ltd.
Regarding the accuracy of electrical instruments, there are seven levels of accuracy, as shown in the table below:
| Accuracy Level | Description |
|----------------|-------------|
| 0.1 | Standard |
| 0.2 | Standard |
| 0.5 | Laboratory |
| 1.0 | Laboratory |
| 1.5 | Engineering |
| 2.5 | Engineering |
| 5.0 | General Use |
The accuracy of a meter depends not only on its accuracy level but also on its range. For optimal accuracy, the range should cover approximately 2/3 of the full scale. Multimeters are versatile and portable tools that can measure DC current, DC voltage, AC voltage, and resistance. Some advanced models can measure capacitance, power, and even transistor parameters. As such, they are indispensable for electricians. Multimeters are available in both analog and digital formats.
By understanding the features and brands of these instruments, electricians can better equip themselves with the right tools for their work.