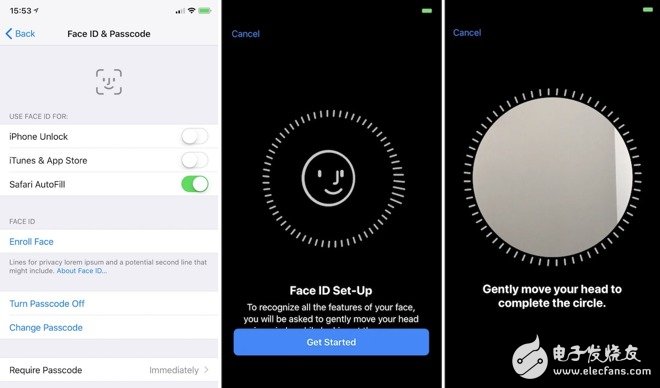
The iPhone X, unveiled during a grand Apple event last night, marked the 10th anniversary of the iconic iPhone. Known for his signature "one more thing" reveal, Steve Jobs' legacy was honored as Apple introduced a groundbreaking feature: Face ID, an advanced facial recognition system that replaced the traditional Touch ID. Understanding Face Recognition Technology Face recognition technology typically involves three main steps: face detection, feature extraction, and face recognition. Face Detection: This process identifies and isolates a face within an image. It often uses algorithms like Haar features and Adaboost to train a cascade classifier, which scans the image in blocks to determine if a face is present. Feature Extraction: Once a face is detected, the system extracts key facial features, converting them into numerical data that can be used for comparison. These features are generally categorized into two types: geometric and appearance-based. Geometric features involve measurements such as distances between facial landmarks, while appearance-based features focus on texture and color patterns. Face Recognition: This step compares the extracted facial features with those stored in a database. It can be further divided into two types: verification (1:1 matching) and identification (1:N matching). Verification checks whether a person matches a specific identity, while identification determines who a person is from a group of known identities. Face ID on the iPhone X Unlike iris scanning used by other companies, Apple’s Face ID uses a combination of infrared sensors, a dot projector, and a front-facing camera to create a detailed 3D map of the user's face. This system projects over 30,000 invisible light points onto the face, capturing depth information that is unique to each individual. The TrueDepth camera system, integrated into the iPhone X’s notch, works alongside the A11 Bionic chip and neural engine to process this data quickly and securely. This makes Face ID not only faster but also more accurate than previous biometric technologies. The innovation behind Face ID lies in its high-resolution sensor and camera setup. Face ID is significantly more secure than Touch ID, with a false match rate of just one in a million, compared to one in 50,000 for fingerprint recognition. It also includes an attention detection feature, ensuring the user is looking directly at the device before unlocking. Even changes like wearing glasses, growing a beard, or changing hairstyles do not affect the accuracy of the system. During the setup process, users are prompted to move their face around the screen to capture all angles. Infrared technology ensures the system works even in low-light conditions, making it highly reliable. Face ID is compatible with Apple Pay and third-party apps that previously supported Touch ID, making it a seamless upgrade. While Apple wasn’t the first to introduce fingerprint recognition, it was the company that made it a standard across smartphones. With the iPhone X, Apple chose to move away from Touch ID entirely, signaling a shift toward facial recognition as the future of mobile security. Applications of Face Recognition Technology Face recognition has a wide range of applications, from security to convenience. One of the most common use cases is 1:1 authentication, where a person’s face is matched against a pre-recorded image for real-time verification. This is widely used in banking, travel, and online services. Compared to fingerprint or iris scanning, face recognition offers a non-contact experience, improving both speed and hygiene. Another major application is 1:N recognition, where a single face is compared against a database of many people. This is commonly used in public safety, access control, and law enforcement. For example, a police department in Chongqing used facial recognition to identify 69 suspects within 40 days, achieving a success rate 200 times higher than manual methods. The third key area is live face verification, which ensures that the person using a service is genuinely present. This is crucial for online account registration, remote banking, and secure transactions. Many banks and financial institutions have already adopted this technology to enhance security and reduce fraud. As the technology continues to evolve, face recognition is expanding beyond digital platforms. From unmanned supermarkets to airport check-ins and hotel check-ins, the applications are becoming more diverse. With increasing adoption, face recognition is set to become an essential part of daily life, offering greater convenience and efficiency. Photovoltaic Bracket,supporting structure ground solar,ground solar mounting structure,solar mounting structure,solar ground mount Hebei Shuobiao New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.pvbracketsystem.com