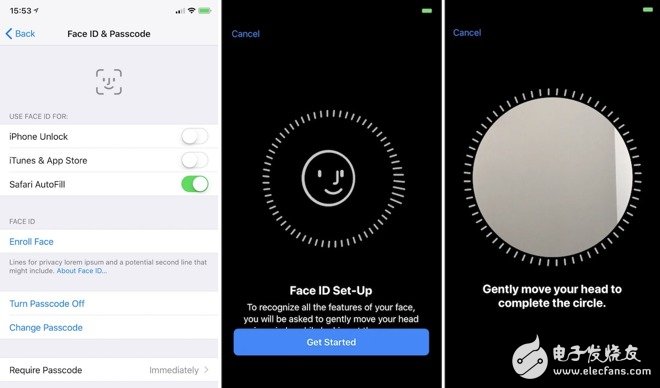
The iPhone X, launched during the special 10th-anniversary event by Steve Jobs, introduced a groundbreaking feature that changed the way users interact with their devices—Face ID. This new facial recognition technology, revealed with the famous "one more thing" moment, brought an advanced and secure method of unlocking the phone using your face. Understanding Face Recognition Technology Face recognition is typically divided into three main stages: face detection, feature extraction, and face recognition. Face Detection: This step involves identifying and isolating a face within an image. It often uses algorithms like Haar features and Adaboost to train a cascade classifier, which helps detect facial regions in an image. Once a region passes through this classifier, it's recognized as a face. Feature Extraction: After detecting the face, the system extracts key features that can be used for identification. These features are numerical representations of the unique characteristics of a person’s face. Commonly, these features fall into two categories: geometric and appearance-based. Geometric features include distances between facial landmarks, such as the eyes, nose, and mouth. These are computationally efficient but may not capture all nuances. Appearance-based features, on the other hand, use texture and pixel data for more detailed analysis. Face Recognition: This final stage compares the extracted facial features with those stored in a database. If the similarity score is high enough, the system confirms the identity. This process can be either verification (1:1) or identification (1:N), depending on the application. Face ID on iPhone X Unlike iris scanning used by some competitors, Apple’s Face ID uses a sophisticated TrueDepth camera system. This includes over 30,000 invisible infrared dots projected onto the user’s face, creating a detailed depth map. The system then uses infrared scanning to match this map with the stored data, ensuring a secure and fast unlock experience. The system is integrated with the A11 Bionic chip and uses neural networks to improve accuracy and speed. It also includes attention detection, meaning the device only unlocks when the user is looking directly at it. Even if you're wearing glasses, changing your hairstyle, or growing a beard, Face ID remains highly accurate. The innovation behind Face ID lies in the advanced sensors and cameras embedded in the “Liu Hai†area. Face ID has a false acceptance rate of just one in a million, compared to Touch ID’s one in 50,000. This makes it significantly more secure. During setup, users are guided to rotate their face inside a circle, allowing the system to capture every angle. Infrared light is invisible to the human eye but can be detected by the camera even in low-light conditions. This ensures that Face ID works reliably in various environments. Face ID is also compatible with Apple Pay and third-party apps that previously supported Touch ID. While fingerprint recognition was first introduced by Apple on the iPhone 5S, it was Apple that made it a standard across the industry. Now, they’ve moved on to a more advanced and secure solution: facial recognition. Applications of Face Recognition Technology Face recognition has a wide range of applications today. One of the most common is 1:1 authentication, where a person’s face is matched against a known identity. This is widely used for real-name verification and offers the advantage of being contactless, making it faster and safer than traditional methods. Another important use is 1:N authentication, where the system identifies whether a person belongs to a specific group. This is commonly used in security systems, such as access control in offices or public places. For example, a police department in Chongqing used face recognition to identify 69 suspects in just 40 days, a task that would have taken much longer manually. Finally, there's in vivo testing, which ensures that the person interacting with a system is a real, living individual. This is crucial for financial services and account verification. Many banks across China now use face recognition for remote authentication, enabling customers to open accounts or access ATMs without visiting a branch. As the technology continues to evolve, its applications are expanding from online platforms to offline environments. Unmanned supermarkets, airport check-ins, and hotel check-ins are just a few examples of how face recognition is becoming part of daily life. With continued advancements, we can expect face recognition to become even more integrated into our routines, offering greater convenience and security. Photovoltaic Dual-Axis Tracking Bracket Photovoltaic Dual-Axis Tracking Bracket,Completed Double axis System,Double axis System application,components of Dual Axis Solar Trackers Hebei Shuobiao New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.pvbracketsystem.com