steel Signal Pole,Traffic Signal Pole,steel Sign Post,Monitor Pole JIANGSU XINJINLEI STEEL INDUSTRY CO.,LTD , https://www.chinasteelpole.com
Agv car design internal structure diagram, agv car working principle _ positioning method _ features and guidance
**How AGV Cars Work**
AGV (Automated Guided Vehicle) guidance involves calculating the actual control command for the vehicle based on position data from its sensors. This means setting a target speed and steering angle, which is essentially the core of AGV control. In short, AGV guidance is about tracking a specific path. There are various methods to guide an AGV. One common approach is using the center point of the guiding sensor as a reference and tracking a virtual point on a magnetic strip. The goal of the AGV is to adjust the rotation speed of the wheels to change direction by detecting the relative position between the reference point and the virtual point, aiming to keep the reference directly above the virtual point. This allows the AGV to consistently follow the designated path.
Once the AGV receives a material handling instruction, the control system calculates, plans, and analyzes based on the stored map and the current location and direction of the vehicle. It then selects the optimal route and automatically controls the movement and steering of the AGV. Upon reaching the loading position, it accurately parks, and the transfer mechanism moves to complete the loading process. The AGV then drives to the unloading point, parks again, and the transfer mechanism completes the unloading. After that, it reports its status and position back to the control system and heads to the standby area until a new order is received.

**Features of AGV Cars**
1. **High Level of Automation**:
AGVs are controlled by computers, electronic control systems, magnetic sensors, and laser reflectors. When a workshop needs materials, staff input the information into a computer terminal, which sends it to the central control room. Technicians then send instructions to the AGV, which follows them with the help of electronic equipment.
2. **Automatic Charging**:
When the battery level is low, the AGV sends a charging request to the system. Once approved, it automatically queues up for charging. AGVs typically have long-lasting batteries (over 2 years) and can operate for about 4 hours after just 15 minutes of charging.
3. **Aesthetic Design**:
AGVs improve the visual appeal of a facility, enhancing the company's image and professional appearance.
4. **Space Efficiency**:
AGVs can move back and forth in different areas of the workshop, reducing floor space requirements.
**Structure of an AGV Trolley**
1. **Chassis**:
The physical body of the AGV, including the frame and mechanical components, serves as the base for other parts.
2. **Power Unit**:
Most AGVs are powered by 24V or 48V DC batteries, often lead-acid or lithium-ion. Lithium batteries allow for automatic charging and 24-hour operation.
3. **Drive System**:
Components like wheels, gearboxes, brakes, motors, and speed controllers ensure smooth operation. Commands are issued via computer or manual control, and the system adjusts speed, direction, and braking accordingly.
4. **Guidance System**:
Combining magnetic sensors and landmark sensors, this system enables the AGV to navigate forward, backward, turn, and exit paths.
5. **Controller**:
The controller receives commands from the control center and executes them while sending real-time feedback on position and speed.
6. **Communication Device**:
Allows data exchange between the AGV and the ground control station or monitoring equipment.
7. **Safety Devices**:
Includes obstacle sensors, anti-collision mechanisms, and emergency stop switches to protect people, the AGV, and other equipment.
8. **Carrier**:
A traction bar used to transport goods directly.
9. **Information Processing Unit**:
Enables real-time monitoring and communication between the AGV and the control center.

**AGV Guidance Methods**
AGV guidance refers to how the vehicle determines its direction and path. There are two main categories: pre-defined path mode and free path mode.
**(1) External Path Guidance**
This method uses physical markers such as magnetic tapes, reflective strips, or optical guides. The AGV detects these signals and follows the path accordingly.
- **Reflective Guidance**:
A luminescent tape or paint is laid on the ground, and a reflective light sensor on the vehicle detects it, adjusting the direction dynamically.
- **Magnetic Guidance**:
A metal magnetic tape is placed on the ground, and a magnetic sensor on the AGV detects the field, adjusting the direction based on deviation.
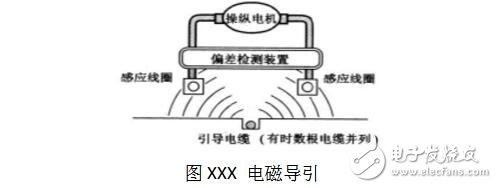
**Electromagnetic Induction Guidance**
This is one of the most widely used methods. A cable is buried in the floor, generating a magnetic field. Two induction coils on the AGV detect the signal, allowing the system to calculate the deviation and correct the path.
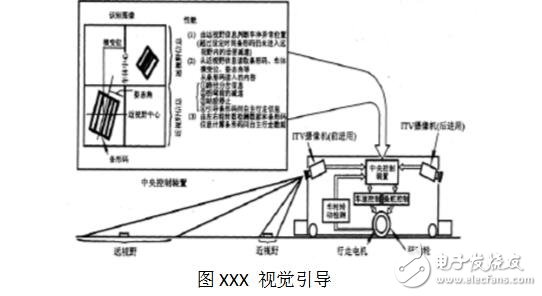
**Visual Guidance**
AGVs use cameras and sensors to recognize signs, reflectors, or markers along the path. This method offers high flexibility since no physical path is required. As image processing technology advances, this method is becoming increasingly practical.
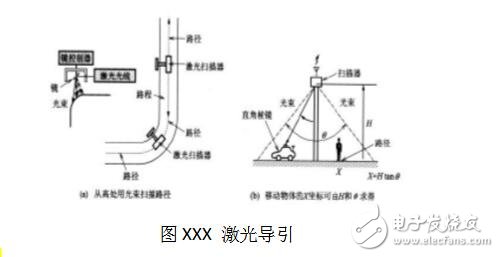
**Laser Guidance**
AGVs equipped with laser scanners detect highly reflective markers on walls or pillars. The system calculates the vehicle’s position and orientation, enabling precise navigation. Similar principles apply to infrared and ultrasonic guidance systems.
**AGV Positioning Methods**
To ensure accurate positioning, different sensors are used:
- **Photoelectric Sensor-Based Positioning**:
Uses the photoelectric effect, offering a long detection range but lower accuracy.
- **Eddy Current Sensor-Based Positioning**:
Provides high precision and sensitivity, though it has a larger size and may interfere with electromagnetic systems.
- **Photoelectric Pair Tube Method**:
Offers high accuracy (up to 1.5mm), but lacks control after the final positioning.
- **Sensor Combination Method**:
Combines light guidance and fine positioning for high accuracy, though it requires more complex equipment.
**Recommended Reading**
- How does the AGV car work?
- Development status and application field analysis of AGV cars
- How to achieve positioning of AGV cars
- Characteristics and comparative analysis of RGV trolleys and AGV trolleys
Yixing Futao Metal Structural Unit Co. Ltd. is com manded of Jiangsu Futao Group.
It is located in the beach of scenic and rich Taihu Yixing with good transport service.
The company is well equipped with advanced manufacturing facilities.
We own a large-sized numerical control hydraulic pressure folding machine with once folding length 16,000mm and the thickness 2-25mm.
We also equipped with a series of numerical control conveyor systems of flattening, cutting, folding and auto-welding, we could manufacture all kinds of steel poles and steel towers.
Our main products: high & medium mast lighting, road lighting, power poles, sight lamps, courtyard lamps, lawn lamps, traffic signal poles, monitor poles, microwave communication poles, etc. Our manufacturing process has been ISO9001 certified and we were honored with the title of the AAA grade certificate of goodwill"
Presently 95% of our products are far exported to Europe, America, Middle East, and Southeast Asia, and have enjoyed great reputation from our customers,
So we know the demand of different countries and different customers.
We are greatly honored to invite you to visit our factory and cheerfully look forward to cooperating with you.