Initial schematic transfer Passing the schematic through the netlist file to the layout environment also passes device information, netlists, layout information, and initial trace width settings. Here are some recommended steps for the layout design phase: 1. Set the grid and unit to appropriate values. In order to achieve finer layout control of components and traces, the device grid, copper grid, via grid, and SMD grid can be designed to 1 mil. 2. Set the circuit board blanks and vias to the required values. PCB manufacturers may have specific minimum or nominal recommended values ​​for blind and buried vias. 3. Set the appropriate pad/via parameters based on PCB manufacturer capabilities. Most PCB manufacturers can support smaller vias with a hole diameter of 10 mils and a pad diameter of 20 mils. 4. Set design rules as required. 5. Set custom shortcuts for common layers to quickly switch layers (and create vias) while routing. Dealing with errors during schematic transfer A common mistake in schematic transfer is the absence or incorrect packaging assignment. have to be aware of is: If there is a device in the schematic without encapsulation, an alert message pops up indicating that the virtual component cannot be exported. In this case, no default package information is passed to the layout, and the components are simply removed from the layout. If the encapsulation passes but the correct encapsulation shape cannot be correctly matched, an alarm message indicating a mismatch will also be generated during the transfer. Correct the package assignment in the schematic or create a valid package for any device. Correct and then perform forward labeling steps to update and synchronize design information. Update design by tagging Annotation is the process of passing design changes from a schematic to a layout or from a layout to a schematic. Backward labeling (layout to schematic) and forward labeling (schematic to layout) are key to maintaining design accuracy. To protect the work that has already been done, you need to back up and archive the current version of the schematic and layout files before any important forward or reverse labeling steps. Do not try to make changes simultaneously in schematics and layouts. Only make changes to one part of the design (either schematic or layout), and then perform the correct labeling steps to synchronize the design data. Renumber devices Device renumbering is a function that renumbers components on a PCB in a specific order. The reference numbers should be sorted in the direction from top to bottom and left to right on the PCB. This makes it easier to position the device on the board during assembly, testing, and troubleshooting. Process last-minute device or netlist changes Last-minute changes to the PCB device or netlist are undesirable, but sometimes have to be due to device availability problems or the detection of last-minute design errors. If you need to change the component or netlist, you should do it in the schematic and then mark it in the forward direction to the layout tool. Here are some tips: 1. If adding a new device (such as adding a pull-up resistor to the open-drain output) after the layout design begins, add a resistor and network to the design from the schematic. After positive labeling, the resistor will be displayed as an unlayed component outside the board outline, and the flying line indicates the connection network. Next, move the components to the circuit board frame and perform normal wiring. 2. The backward labeling and reference label changes can work well together, such as renumbering the rear layout. Selecting a positioning device by highlighting One way to view specific components or traces in a schematic during PCB layout is to use the 'Highlight Select' function. This feature allows you to select a component or a trace (or multiple objects) and view their position in the schematic. This feature is especially useful when matching bypass capacitors and their corresponding IC connections. Conversely, you can also locate specific elements or traces in the layout while you are browsing the schematic. Film Covered Flat Aluminium Wire
Fiber glass film covered enameled aluminum flat wire
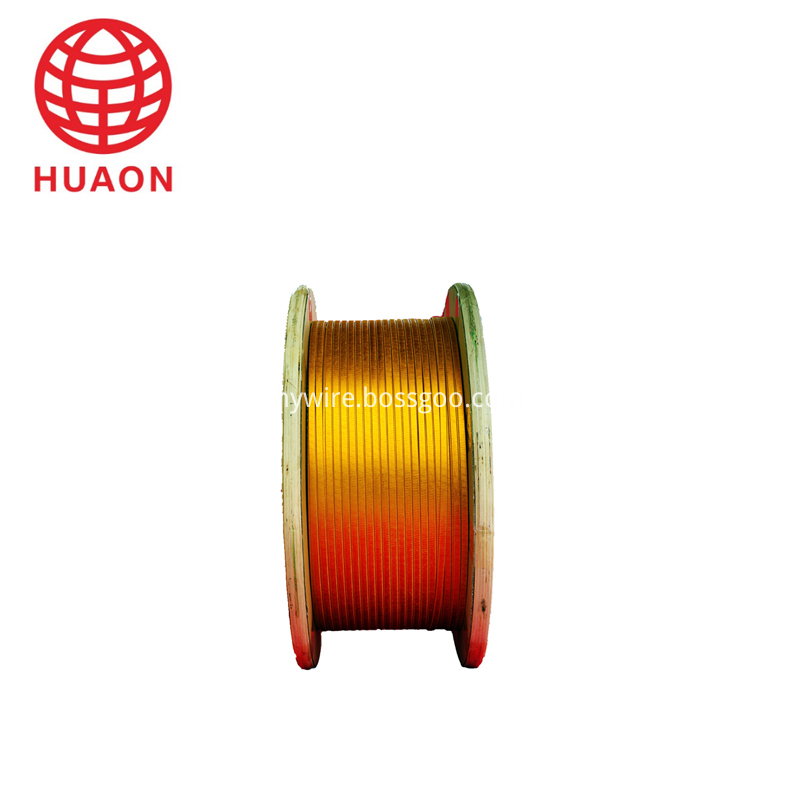
The product is the premium copper or aluminum to be enameled, then to be wrapped with polyester film or polyimide film so as to enhance the breakdown voltage of enameled wire. It has the advantages of thin insulation thickness, high voltage resistance. The product is the ideal material for electrical instruments of small size, large power, high reliability.
Copper or Aluminum rectangular Wire
Narrow side size a : 1.00 mm-5.60 mm
Broad side size b : 2.00 mm-16.00 mm
Film Covered Copper Wire,Film Covered Flat Aluminium Wire,Covered Flat Magnet Wire,Fiberglass Covered Wire HENAN HUAYANG ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY GROUP CO.,LTD , https://www.huaonwire.com
About Film Covered Flat Aluminium Wire
