Twisted pair Twisted Pair (TP: Twisted Pairwire) is the most commonly used transmission medium in integrated wiring projects. The twisted pair consists of two copper wires with an insulating protective layer. Twisting two insulated copper wires with each other at a certain density can reduce the degree of signal interference. The electric wave radiated by each wire during transmission will be cancelled by the electric wave emitted by the other wire. Twisted pair is generally made of two 22 to 26 insulated copper wires intertwined with each other. If you put one or more pairs of twisted pairs in an insulating sleeve, it becomes a twisted pair cable. In twisted pair cables (also called twisted pair cables), different pairs have different twist lengths. Generally speaking, the twist length is within 38.1cm to 14cm, twisted counterclockwise, and the adjacent pairs The twist length is more than 12.7cm. Compared with other transmission media, twisted-pair cable is subject to certain restrictions in terms of transmission distance, channel width and data transmission speed, but the price is relatively low. At present, twisted pair can be divided into unshielded twisted pair (UTP: Unshilded Twisted Pair) and shielded twisted pair (STP: Shielded Twisted Pair). Although the twisted pair is mainly used to transmit analog voice information, it is also suitable for digital signal transmission, especially for shorter distance information transmission. During transmission, the signal attenuation is relatively large, and waveform distortion occurs. The bandwidth of the LAN using twisted pair depends on the quality, length and transmission technology of the wire used. As long as the twisted pair is carefully selected and installed, a reliable transmission rate of several million bits per second can be achieved within a limited distance. When the distance is short and special electronic transmission technology is adopted, the transmission rate can reach 100Mbps ~ 155Mbps. Because the information is transmitted to the surroundings when using twisted pairs to transmit information, the information is easily eavesdropped, so it needs to be shielded at an extra cost. The outer layer of the shielded twisted pair cable is wrapped by aluminum to reduce the radiation, but it cannot completely eliminate the radiation. Shielded twisted pair cables are relatively expensive, and installation is more difficult than unshielded twisted pair cables. Similar to the coaxial cable, it must be equipped with a special connector that supports the shielding function and the corresponding installation technology. But it has a higher transmission rate, which can reach 155Mbps within 100 meters. In addition, unshielded twisted pair cable has the following advantages: (1) No shielding jacket, small diameter, saving occupied space; 2. Specifications EIA / TIA defines five different quality models for twisted pair cables. Computer network integrated wiring uses the third, fourth, and fifth categories. The five models are as follows: 1. The first category: mainly used to transmit voice (the first category is mainly used for telephone cables before the early 1980s), not for data transmission. Twisted-pair cable is divided into two categories: shielded twisted-pair cable and unshielded twisted-pair cable. In these two categories, it is divided into 100-ohm cable, double-body cable, large logarithmic cable, and 150-ohm shielded cable. There are many specific models, as shown in Figure 1. In the figure, AWG represents the American cable specification. 3. Performance index For twisted pair, users are most concerned about several indicators that characterize its performance. These indicators include attenuation, near-end crosstalk, impedance characteristics, distributed capacitance, and DC resistance. (1) Attenuation Attenuation (AttenuaTIon) is a measure of signal loss along the link. The attenuation is related to the length of the cable. As the length increases, the signal attenuation also increases. Attenuation uses "db" as the unit, which represents the ratio of the signal strength of the source transmitting end to the signal strength of the receiving end. Since the attenuation varies with frequency, the attenuation at all frequencies in the application range should be measured. Table 1 Attenuation limits at various frequencies when various connections are at maximum length Table 2 NEXT attenuation limits at specific frequencies The above two indexes are the main content of TSB67 test, but some types of testers can also give indexes such as DC resistance, characteristic impedance, and attenuation crosstalk ratio. 4. Test data 100 ohm 4 pairs of unshielded twisted pair cables are classified into category 3, category 4, category 5 and super category 5. The main performance indicators are attenuation, distributed capacitance, DC resistance, DC resistance deviation, impedance characteristics, return loss, and near-end crosstalk. The standard test data is shown in Table 1. Table 3 Standard test data of twisted pair Rate minus (unit db) 5% Same as above 5% Same as above 5% (b) Impedance characteristics 12db 43db Same as above 12db 58db Same as above 23db 64db 5. Commonly used twisted pair cables The most commonly used twisted pair cables in integrated wiring are the following: 1. Category 5 4 pairs of unshielded twisted pair It is a solid bare copper conductor with a cable size of 24 in the United States. It is made of vinyl fluoride as an insulating material and has a transmission frequency of 100MHz. The composition of the wires is shown in Table 4, and the physical structure is shown in Figure 2. Table 4 Wire color coding The electrical characteristics are shown in Table 5. Among them, "9.38 ohm MAX. Per100m @ 20 ℃" means that at a constant temperature of 20 ℃, the resistance per 100 meters of twisted pair is 9.38 ohm (similar in the table below). Table 5 Electrical characteristics of 5 pairs of 4 pairs of unshielded twisted pair It is a bare copper conductor with a wire gauge of 24 in the United States. It is made of vinyl fluoride as an insulating material and has a 24AWG TPG drain wire inside. The transmission frequency reaches 100MHz, the composition of the wires is shown in Table 6, the physical structure is shown in Figure 3, and the electrical characteristics are shown in Table 7. The meaning of the shielding item "0.002 [0.051] aluminum / polyester tape minimum overlap @ 20 ℃ and a 24AWG TPC drain wire in Table 6 is: The thickness of the shielding layer is 0.002 cm or 0.051 inches. Table 6 Wire color coding 1 It consists of 4 pairs of wires and a 26AWG TPC drain wire, with a transmission frequency of 100MHz. The composition of the wires is shown in Table 8, the physical structure is shown in Figure 4, and the electrical characteristics are shown in Table 9. Table 8 Wire color coding It is composed of 4 pairs of wires and is used for high-speed data transmission. It is suitable for extending the transmission distance and used for interconnection or patch cords. The transmission rate reaches 100MHz. The composition of the wires is shown in Table 9, its physical structure is shown in Figure 5, and its electrical characteristics are shown in Table 10. Table 9 Wire color coding The Category 5 cabling system is an unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling system, and its "link" and "channel" performance tests show that it exceeds TIA / EIA568 Category 5 cable requirements. Compared with the ordinary UTP category 5, it has smaller attenuation and less crosstalk. It also has higher attenuation to crosstalk ratio (ACR) and signal to noise ratio (SRL), smaller delay error, and improved performance. It has four major advantages: (1) Provide a solid network foundation, which can facilitate the transfer and update of network technology. Compared with Category 5 cables, Category 5 has great improvements in the four main indicators of near-end crosstalk, total crosstalk, attenuation and signal-to-noise ratio. Near-end crosstalk (NEXT) is the most important criterion for evaluating performance. A high-speed LAN is synchronized when transmitting and receiving data. NEXT is an interference signal generated when transmission and reception are performed simultaneously. The unit of NEXT is db, which represents the ratio between the transmitted signal and the crosstalk signal. In ordinary applications, the standard method of measuring NEXT is to use a pair of lines for transmission, and another pair of lines for reception, such as 10BASET and TokenRing, and even 100BASET and 155Mbps ATM. However, sometimes you can also use another two pairs of wires and connect them to another workstation, which can speed up the LAN speed, such as 622Mbps ATM and 1000BASE-T. receive. Using multiple pairs of wires in a cable for transmission will increase the crosstalk of the cable. The current four pairs of category 5 twisted pairs do not consider this situation. Power Sum NEXT is the sum of NEXT generated from multiple transmission ends. If a wiring system can meet the NEXT requirements of Category 5 cables under Power Sum, then it can handle any problems from application sharing to high-speed LAN applications. The NEXT of a Category 5 cabling system is only 1/8 of that required by Category 5 cables. Signal to noise ratio (Structural Return Loss) is a standard to measure the consistency of cable impedance. The change of impedance causes reflection. Part of the energy of the signal is reflected to the sending end, forming noise. SRL is a standard for measuring energy changes. Due to changes in cable structure, impedance changes cause signal energy to change. The less energy reflected, the more complete the transmitted signal and the less noise on the cable. Compared with the ordinary Category 5 twisted pair, when the Category 5 system runs at 100MHz, it provides users with a margin of 8db near-end crosstalk.The interference of the user's equipment is only 1/4 of the ordinary Category 5 line system. The system has stronger independence and reliability.
Welcome to the Night lights Store, where you'll find great prices on a wide range of different night lights for your home.
Users: Suitable for all kinds of persons to use. No matter you are a student or a white collar, you will like this natural and comfortable light.
Light sensor lamp, energy-saving light, bringing your life great convenience.
LED Night Light,LED Socket Night Light,Portable LED Night Light,LED USB Night Light,Colorful Night Light Shenzhen Superlight Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.superlighttech.com
(2) Light weight, easy to bend and easy to install;
(3) Minimize or eliminate crosstalk;
(4) Flame retardant;
(5) It has independence and flexibility and is suitable for structured integrated wiring.
2. The second type: the transmission frequency is 1MHz, which is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 4Mbps, which is common in the old token network using the 4Mbps standard token transfer protocol.
3. The third category: refers to the cables currently specified in the ANSI and EIA / TIA568 standards. The transmission frequency of the cable is 16MHz, which is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 10Mbps, and is mainly used for 10base-T.
4. The fourth category: The transmission frequency of this type of cable is 20MHz, which is used for voice transmission and data transmission with the highest transmission rate of 16Mbps, which is mainly used for token-based LAN and 10base-T / 100base-T.
5. The fifth category: this type of cable has increased winding density, and a high-quality insulating material is coated. The transmission frequency is 100MHz. It is used for voice transmission and data transmission with a maximum transmission rate of 100Mbps. It is mainly used for 100base-T and 10base-T network, which is the most commonly used Ethernet cable. 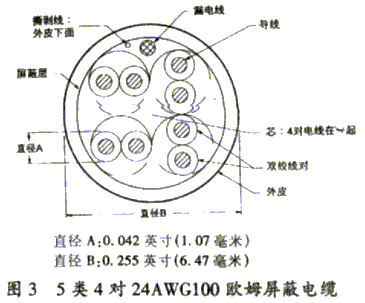
(2) Near-end crosstalk Crosstalk is divided into near-end crosstalk and far-end crosstalk (FEXT). The tester mainly measures NEXT. Due to line loss, the effect of FEXT magnitude is small. Near-end crosstalk (NEXT) loss measures the signal coupling from one pair of wires to another pair of wires in a UTP link. For UTP links, NEXT is a key performance indicator and the most difficult to accurately measure. As the signal frequency increases, the difficulty of its measurement will increase.
NEXT does not indicate the crosstalk value generated at the near endpoint, it only indicates the crosstalk value measured at the near endpoint. This value will vary with the length of the cable, the longer the cable, the smaller the value becomes. At the same time, the signal at the sending end will also be attenuated, and the crosstalk to other pairs will be relatively small. Experiments show that only NEXT measured within 40 meters is more real. If the other end is an information socket farther than 40 meters, it will produce a certain degree of crosstalk, but the tester may not be able to measure this crosstalk value. Therefore, it is best to perform NEXT measurements at both endpoints. The current testers are equipped with corresponding equipment, so that the NEXT value at both ends can be measured at one end of the link. Refer to Table 1 and Table 2 for the NEXT test results. Frequency (MHz) Maximum rate minus 20ºC Channel (100 meters) Link (90 meters) Category 3 Category 4 Category 5 Category 3 Category 4 Category 5 1 4.2 2.6 2.5 3.2 2.2 2.1 4 7.3 4.8 4.5 6.1 4.3 4.0 8 10.2 6.7 6.3 8.8 6 5.7 10 11.5 7.5 7.0 10 6.8 6.3 16 14.9 9.9 9.2 13.2 8.8 8.2 20 11 10.3 9.9 9.2 25 11.4 10.3 31.25 12.8 11.5 62.5 18.5 16.7 100 twenty four 21.6 Frequency (MHz) Min NEXT Channel (100 meters) Link (90 meters) Category 3 Category 4 Category 5 Category 3 Category 4 Category 5 1 39.1 53.3 60.0 40.1 54.7 60.0 4 29.3 43.3 50.6 30.7 45.1 51.8 8 24.3 38.2 45.6 25.9 40.2 47.1 10 22.7 36.6 44.0 24.3 38.6 45.5 16 19.3 33.1 40.6 twenty one 35.3 42.3 20 31.4 39.0 33.7 40.7 25 37.4 39.1 31.25 35.7 37.6 62.5 30.6 32.7 100 27.1 29.3
(3) DC resistance TSB67 does not have this parameter. The DC loop resistance consumes part of the signal and converts it into heat. It refers to the sum of the resistance of a pair of wires. The DC resistance of the twisted pair of 11801 specifications should not be greater than 19.2 ohms. The difference between each pair can not be too large (less than 0.1 ohm), otherwise it indicates poor contact, you must check the connection point.
(4) Characteristic impedance Different from the loop DC resistance, the characteristic impedance includes resistance and inductance impedance and capacitance impedance with a frequency of 1 to 100 MHz, which is related to the distance between a pair of wires and the electrical performance of the insulator. Various cables have different characteristic impedances, while twisted pair cables have 100 ohms, 120 ohms and 150 ohms.
(5) Attenuation crosstalk ratio (ACR)
In some frequency ranges, the proportional relationship between crosstalk and attenuation is another important parameter that reflects cable performance. ACR is also sometimes expressed as a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR: Signal-Noice raTIo), which is calculated from the difference between the worst attenuation and the NEXT value. ACR value is larger, which means that the ability to resist interference is stronger. General system requirements are at least greater than 10 decibels.
(6) Cable characteristics The quality of the communication channel is described by its cable characteristics. SNR is a measure of data signal strength considering interference signals. If the SNR is too low, the receiver will not be able to distinguish between the data signal and the noise signal when the data signal is received, which will eventually cause data errors. Therefore, in order to limit data errors to a certain range, a minimum acceptable SNR must be defined.
(a) Types of Distributed capacitance
(Measured in 1khz) DC Resistance
20ºC measurement correction value DC resistance deviation
Measurement correction value at 20º Category 3 <2.320sqrt (f) + 0.238 (f) <330pf / 100m <9.38 ohms / 100 meters Category 4 <2.050sqrt (f) + 0.1 (f) <330pf / 100m Category 5 <1.9267sqrt (f) + 0.075 (f) <330pf / 100m Types of
1Mhz to the highest reference frequency value Return loss measurement length> 100 meters Near-end crosstalk measurement length> 100 meters Category 3 100 ohms + 15% Category 4 Category 5 Wire pair Color code 1 White / blue // blue 2 White / orange // orange 3 White / green // green 4 White / brown // brown
Figure 2 Category 5 4 pairs of unshielded twisted pair 
Frequency requirement (Hz) impedance Attenuation value
(dh / 100) Max NEXT (db)
(Worst pair) DC impedance 256K - 1.1 - 9.38 ohms
MAX.Per
100m @ 20ºC 512K - 1.5 - 772K - 1.8 66 1M 85 ~ 115
ohm 2.1 64 4M 4.3 55 10M 6.6 49 16M 8.2 46 20M 9.2 44 31.25M 11.8 42 62.50M 17.1 37 100M 22.0 34
2. Category 5 4 pair 24AWG 100 ohm shielded cable
· @ 20 ℃ means at a constant temperature of 20 ℃. Wire pair Color code shield White / blue // blue 0.002 [0.051]
Aluminum / polyester tape minimum overlap @ 20º and one
24AWG TPC
Leaky wires. 2 White / orange // orange 3 White / green // green 4 White / brown // brown
Figure 3 Category 5 4 pair 24AWG 100 ohm shielded cable 
Table 7 Category 5 4 pairs of 24AWG 100 ohm shielded cable electrical characteristics Frequency requirement (Hz) impedance Attenuation value
(dh / 100) Max NEXT (db)
(Worst pair) DC impedance 256K - 1.1 - 9.38 ohms
MAX.Per
100m @ 20ºC 512K - 1.5 - 772K - 1.8 66 1M 85 ~ 115
ohm 2.1 64 4M 4.3 55 10M 6.6 49 16M 8.2 46 20M 9.2 44 31.25M 11.8 42 62.50M 17.1 37 100M 22.0 34
3. Category 5 4 pair 26AWG shielded flexible wire Wire pair Color code shield 1 White / blue // blue 0.002 [0.051]
A section of 26AWG TPC in aluminum / polyester tape foil
Leaky wires. 2 White / orange // orange 3 White / green // green 4 White / brown // brown
Figure 3 Category 5 4 pairs of 24AWG unshielded wire electrical characteristics 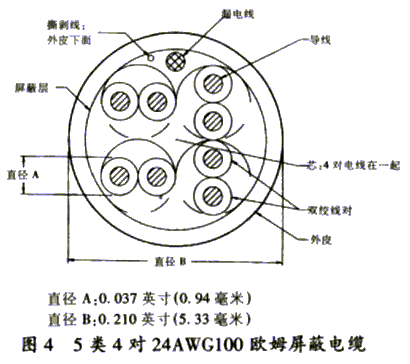
4. Category 5 4 pair 24AWG unshielded flexible wire Wire pair Color code 1 White / blue // blue 2 White / orange // orange 3 White / green // green 4 White / brown // brown
Figure 5 Category 5 4 pair 24WAG100 unshielded flexible cord 
Table 10 Electrical characteristics of 5 types of 424WAG100 pairs of unshielded flexible cords Frequency requirement (Hz) impedance Attenuation value
(dh / 100) Max NEXT (db)
(Worst pair) DC impedance 256K - - - 8.8 ohm
MAX.Per
100m @ 20ºC 512K - - - 772K - 2.0 66 1M 85 ~ 115
ohm 2.3 64 4M 5.3 55 10M 8.2 49 16M 10.5 46 20M 11.8 44 31.25M 15.4 42 62.50M 22.3 37 100M 28.9 34
(2) Can meet the requirements of most applications, and meet the requirements of low deviation and low crosstalk.
(3) It is considered to be a solution provided for future network applications.
(4) Sufficient performance margin brings convenience for installation and testing.
Made of high-quality material, durable enough for long time daily use.
Easy and convenient to use and install.